HUBLE METHODS
Culture of MLO-A5 and MLO-Y4 osteocyte cell lines
MLO-A5 and MLO-Y4 are murine cell lines routinely used to study osteocytes1,2. This HubLE Method describes the protocol for the routine culture of these cell lines.
Materials
- Rat tail type-I collagen solution
- 0.02M Acetic acid solution (sterile)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) Ca2+ and Mg2+ free, pH7.4
- Penicillin/Streptomycin
- Foetal bovine serum (FBS)
- Calf serum (CS)
- Complete media (CM): Minimum Essential Medium Eagle – Alpha modification (αMEM)supplemented with penicillin (100U/mL) and streptomycin (100µg/mL) + 2.5%FBS + 2.5%CS
- Trypsin-EDTA
- Dimethyl Sulfoxide (DMSO)
Method [Update]
Tips [Update]
Rat tail type 1 collagen: Use ice-cold pipette tips when working with rat tail type 1 collagen.
Excess collagen solution from the flasks/wells can be reused up to 5 times and should be stored at 4°C. With each use the efficiency of coating may decrease, and increasing coating incubation time is suggested. The coated flasks and plates can also be stored at 4°C for up to a month.
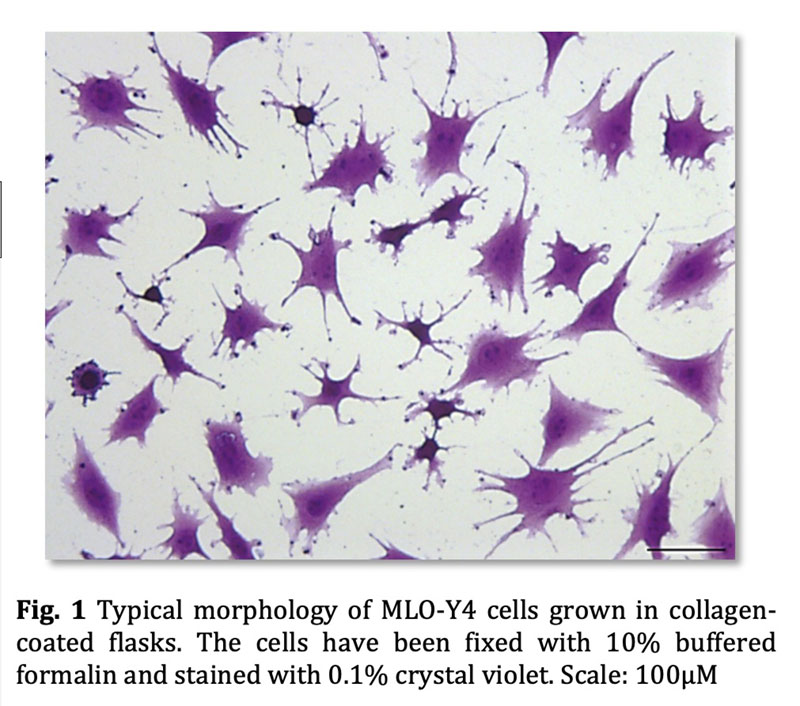
Cells in collagen-coated T75 flasks can be grown till 70% confluence before passaging. MLO-Y4 cells should not be allowed to grow above 70% confluency to maintain their phenotype. Care should be taken to avoid high flow rates during media changes, as osteocyte-like cells are extremely sensitive for fluid flow-derived shear stress.
Typically, 2.0-2.5×106 cells are harvested from a T75 flask with routine seeding of 0.5–1×106 cells per T75 flask.
References [Update]
Kato, Y., Boskey, A., Spevak, L., Dallas, M., Hori, M. & Bonewald, L.F. (2001) Establishment of an osteoid preosteocytelike cell MLO-A5 that spontaneously mineralizes in culture. J Bone Miner Res, 16, 1622-1633.
Kato, Y., Boskey, A., Spevak, L., Dallas, M., Hori, M. & Bonewald, L.F. (2001) Kato, Y., Windle, J.J., Koop, B.A., Mundy, G.R. & Bonewald, L.F. (1997) Establishment of an osteocyte-like cell line, MLO-Y4. J Bone Miner Res, 12, 2014-2023.

Luke Tattersall BSc, PhD
Department of Oncology & Metabolism, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S10 2RX, UK. Email: l.tattersall@sheffield.ac.uk

Karan M. Shah MSc, PhD
Department of Oncology & Metabolism, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, S10 2RX, UK. Email: k.shah@sheffield.ac.uk